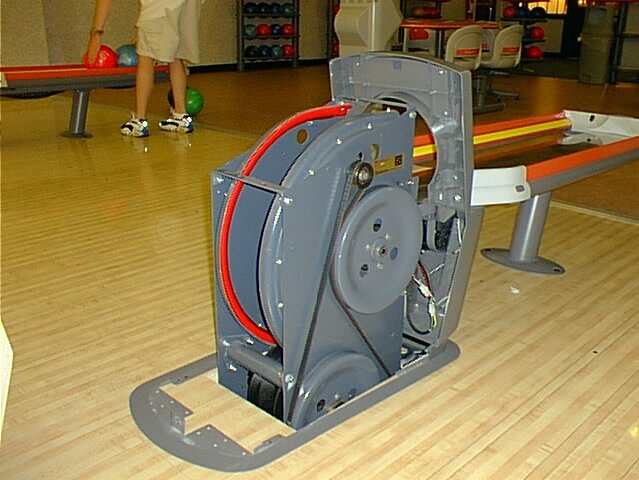
Daily Process Verification
It is critical now more than ever in the game of bowling to verify your lane maintenance procedures on a daily basis. This simply means using your basic senses to ensure the lane machine that is being run has actually performed the task adequately. Why is this you may ask?
Simply put, the daily responsibility of lane maintenance has somewhat shifted away from the operator and directly to the lane machines that are currently being used. Many bowling centers have automated lane machines that move themselves or manual machines that are pre-programmed and the operator simply presses a button while the machine does all of the lane maintenance.
Just remember it is still the responsibility of the operator to ensure the machine has achieved what it was programmed to do. Just because the lane machine went down the lane and returned back to the foul line does not necessarily mean the lane has cleaned and conditioned properly.
Simply training your eyes, ears, and hands to focus on specific aspects of the lane machine as well as the lane surface will give you daily peace of mind and your customers will be more than satisfied with the end result.
If you utilize these simple tips every time you perform lane maintenance your customers will keep coming back for more. The thing that people look for the most in bowling is consistency, not high scoring. However high scoring inevitably evolves from consistency which means there is a way to give your customers both. Just spending an extra ten minutes per day will guarantee your customers satisfaction every time they come to your center to bowl.
Scan the QR code below to view these daily lane maintenance tips.
Sound, sight, and touch will prevent lane maintenance disasters that can occur when everything seems to be operating normally from a lane machine standpoint.
Sound:
Listening to a lane machine while in operation is much like listening to your own personal vehicle every time you start it and proceed to drive. There are different types of noises within all mechanical things that will sound good, bad, or normal. The more you familiarize yourself with the equipment you are running, the quicker you will be able to tell when something is about to fail or already has. Most lane machines have error codes that will shut the machine down in certain situations, but there are a lot of things that can go wrong, and the machine will still appear to be working to the untrained operator.
A great starting point is for you to train yourself and your staff to hear the vacuum motor when the machine is going down the lane and when it turns on and off during operation. Familiarize yourself with the sound of the cleaner pump when the machine is in the cleaning mode. A conventional spray jet pump can have a faulty diaphragm and still spray cleaner, but there will be substantially less volume than what is needed. A peristaltic cleaner pump will change sound as the tubing starts to wear which is a sign that it needs to be changed.
Neither the vacuum motor nor the cleaner pump failing will prompt an error on the lane machine. It will continue to run every lane and you will not know there is a problem until the lanes are turned on for play and by then it will be too late.
Sight:
Visually inspect the lane machine before every use to ensure there is enough lane conditioner, cleaner, and cloth to complete the number of lanes you need to run. If you are operating a battery lane machine, verify there is enough battery power to complete the total number of lanes that are going to be cleaned and conditioned.
Personally confirm that the program settings match the program sheet for the pattern that you will be applying and if applicable perform a volume check for the cleaner output and the oil output for the pattern in question. Proceed to enter the starting sequence to enable the lane machine. Start the lane machine and walk beside it as it travels down lane towards the pin deck.
Pay attention to the data that is displayed on the keypad such as drive speeds, distance traveled, program number being run, and anything else that your lane machine displays. The numbers should always be consistent from lane to lane and if a variance is noticed the operator should stop the machine and investigate why there may be inconsistencies.
Watch the machine as it applies lane cleaner and lane conditioner. Inspect the pin deck area to ensure there is no residue or lane cleaner being left behind and the machine is traveling far enough before it reverses out of the pit. Excess moisture on the pin deck will result in sliding pins, possible out of ranges and reduces scoring due to lack of pin carry. The “Backends” as they are referred to in our industry consist of every inch of the lane past the oil line and up to the pin deck. This area of the lane should be residue free and squeaky clean.
Once the machine returns to the foul line, walk back down the lane and look over the oil pattern that has just been applied. The lane pattern should look relatively smooth and uniform depending on the type of pattern being run. After the machine has returned to the foul line make sure there are no drips of lane oil or cleaner, streaks in the lane pattern, or anything that looks abnormal to what you are used to seeing every day. Once everything has been verified you may continue running the remainder of the lanes.
Touch:
Once the lanes have been cleaned and conditioned, it is always a good idea to at least do a tactile inspection of your backends as well as your lane pattern. This is something lane maintenance personnel have done for decades, and at one part in our history, was the primary inspection regarding the passing or failing of a lane pattern in sanctioned play.
Our Kegel Team has always made a habit of walking our lanes for a visual and tactile inspection after every lane maintenance routine. Walk the length of the lane and locate the end of the oil pattern and confirm all of the lanes have the same look and distance.
Inspect multiple lanes in the backend area to ensure they are clean and free of residue. Use your knuckles as a way to accurately feel the cleanliness of the lane surface by rubbing them across a section of the backend. There should be no marks or film on any portion of the backend of the lane as this will affect carry down and create inconsistent ball motion.
Pick a lane in the middle of the center and use this lane every day as your gauge on what you feel when you run your fingers across the oil pattern at various distances. Start in the head section of the lane eight feet from the foul line. Using your index and middle fingers, lightly place them on the 2 board on one side of the lane and push your fingertips across 2-20 board and get a feel for how the pattern has less oil on the outside of the pattern and more towards the center. Move to the arrow section of the lane and repeat the process. Here you will feel more of a difference between the outside volume versus the inside boards in the lane pattern than you would have at 8 feet. Continue this at 30-35 feet and in the middle of the pattern taper somewhere between 36-44 feey depending on the pattern length.
Most successful lane patterns are crowned in shape or blended from outside to inside by increasing oil volume board-by-board. These patterns will typically be 40-44 feet in length for a standard house pattern and will have a front to back taper of 7-10 feet depending on the lane surface and chemical being used.
If you utilize these simple steps to verify your lane maintenance procedures on a daily basis you can rest assured, you have given your clientele a consistent bowling experience day after day and week after week. As outlined earlier in this article, consistency is the key to happy customers and a successful business operation.
These are but a few suggestions that our lane maintenance personnel uses at every event we do around the world. There are more complex verification procedures that we at Kegel perform at specific events, such as measuring the topography of every lane in the bowling center, monitoring temperature, humidity, and a variety of other things.
In closing, if you are every at an event where a Kegel representative is present, please feel free to approach that individual at anytime to learn more about all of the procedures that we verify to ensure a successful event.
10 Frequently Asked Questions about Conditioning Lanes
Before making any adjustments to the conditioner pattern, make sure that your lane machine is cleaning properly.
Question: Ball reaction is weak after a game and a half. How do I reduce my carry down?
Answer: Typically the applied oil distance forward is too far creating too much conditioner towards the end of the oil pattern. Reduce the applied distance of conditioner and add to the reverse to prevent the loss of durability.
Question: Ball reaction is strong from the beginning and does not weaken making ball reaction unpredictable. How can I tame my back ends down?
Answer: First, try lengthening the pattern, one foot at a time to the desired result. Second is to change to higher speeds earlier in the pattern to raise the level of conditioner at the end of the pattern.
Question: The pattern plays good from the beginning yet loses hold through the night. How do I increase the hold?
Answer: The applied conditioner on the reverse is what creates durability, this area known as the mid-lane provides direction to the breakpoint and dictates score-ability. Starting reverse oil further down the lane increases hold.
Question: My bowler's tell me "the heads dried out". How do I control early hook?
Answer: First, watch ball reaction, bowlers rarely see what they think they see. In most cases the ball actually hooks too early through the mid-lane. Poor lane surface or lack of conditioner in the lay-down area can also be a cause. In this case, slowing the travel speed in the head area on the return will increase the amount of conditioner in this area. Adding loads in Sanction Technology along with a slower machine speed will increase skid through the heads. However, many times today with the amount of conditioner being applied to the "heads", if the ball is hooking early, there are lane surface issues.
Question: If I get the ball right, it "hangs" outside, 2,8,10 city! How do I create more room right?
Answer: This is a hard one to recognize, because it has multiple and opposite causes.
Too much conditioner on the outside (ball skids too far) or in some cases not enough conditioner on the outside (ball loses energy) can cause "hang".
If the ball skids to far, reducing the length and/or volume of the applied conditioner will help.
A wet/dry condition will result in too much skid inside, giving the appearance of "hang" and a loss of energy if the ball enters the dry too early creating a weaker back-end reaction. Many times the amount of conditioner in the middle is the cause of "hang" and not the amount on the outer boards. Reducing the amount of conditioner in the middle, raising the outside, and using speeds to lower the overall height of a pattern will increase ball reaction and create more playable angles.
Adverse lane topography can affect swing. If this is the issue, reducing the outside condition will allow bowlers to play a more direct line to the pocket.
Question: The bowlers seem to move left very quickly because the track dries up. What can I do to prevent this?
Answer: The volume at the end of the pattern should be slightly more than the outside boards. Applying oil to the track on the reverse can provide more durability without greatly affecting overall ball reaction. With Sanction Technology and board-by-board capability, widening loads one board at a time to get the desired affect can provide the quickest way and retain stability.
Question: How do I determine my cleaner ratio?
Answer: The best idea is to phone the manufacturer for their recommendation. All conditioners are different and clean off the lane differently. For example, Defense lane conditioner is usually stripped at a 4 or 5 to 1 ratio, while Offense can be cleaned at 8 or 10 to 1. This is something that you can experiment with, however, it is not recommended to weaken the stripping solution throughout the entire lane to control the back-end reaction. This can cause for poor cleaning and create numerous other issues.
(Note: With the FLEX lane machine, the ability to weaken the cleaner ratio mix ONLY on the back-end is an option to control back-end ball motion. The FLEX lane machine can keep a strong cleaner mix in the front part of the lane where it is needed.)
Question: How does temperature affect my lane conditioner and lane machine?
Answer: If you are using wick machines, it is highly recommended that you store the machine and conditioner in a place where it is room temperature and will remain constant. This will prevent inconsistent flow through the wicks due to changes in viscosity. In some conditioners, a 1-degree change in temperature can affect viscosity by 2 points cps. This is important for those with Sanction Technology to control the pressure and prevent possible damage to the gauge.
Question: Separate or Simultaneous?
Answer: This is an issue related to wick machines more so than Sanction Technology. Most centers try to reduce depletion one of two ways, either running in separate mode or stopping every so many lanes and letting the machine rest. The separate mode is recommended due to the consistent time in between the oil and strip mode. While the lane is being stripped, the wicks have that time to recover and it is the same from lane to lane. A major issue in resting the machine several times across the center is that it creates a stair step effect of gradually less, than more conditioner, repeated across the lanes.
Question: How does buffer brush wear affect my condition and what should be done upon installing a new one?
Answer: The buffer is designed to taper an oil pattern based off the pattern settings and speeds. As a buffer wears the amount of conditioner at the end of a pattern gradually diminishes over time. This is usually not something bowlers notice and will not come to your attention until you are told that you do not have "three units" any longer. Simply put the brush doesn't hold the conditioner as long as when new and "dumps" it further up lane and creates a steeper taper in the pattern. When replacing the buffer after this gradual wear and even though the pattern settings are the same as when the buffer was new, the effect of a new brush will seem dramatic to the average bowler.
It is highly recommended that this be done in August so the change is not taking place mid-season. The frequency of changing the brush is affected by many factors including number of lanes, how good the lane surface is, and what type of lane surface it is. The more friction the faster the wear. Smaller centers with 24 lanes or less may see two years between buffer changes. Centers with 24 lanes and up may change the brush every year to every six months in centers with a lot of lanes.
How to prevent decreased battery life
As we all know, batteries are not created equal and they do require maintenance. It is important that batteries are charged properly and to make sure the source that is using this supplied power is not abused so that they reach their maximum potential. After reading this, you should be familiar with two causes of decreased battery life and some charging standards for Odyssey batteries.
One of the biggest problems that can decrease battery life is a machine that has been abused. When a machine is not kept clean or well maintained, it can cause an overall higher amp draw and result in the battery dropping out faster.
For example, if the vacuum motor has had waste sucked into it, like the images of abused vacuum motors below, this can greatly affect the battery. Damage like this could hinder machine performance and easily cause a NEW set of batteries to do 25 lanes less than it should.
Another battery issue that is often overlooked is whether the charger is giving the batteries a proper charge. This can take into account any portion of the charging mechanism. The Odyssey batteries require different stages of charging which should be as high as 29 volts within the first 30 minutes of being on charge to as low as 27 volts after being on charge for 6-8 hours. If proper charging does not occur, this will also affect the life of your batteries.
Periodic checking of the charging system along with regular maintenance of your lane machine will greatly extend the life of your batteries.
Synthetic Approach Maintenance
Let’s face it; approach maintenance can be a sticky, or slippery, business. There is a fine line to walk when trying to keep the approaches as consistent as possible. Some products offer too much slide causing bowlers to slip while other products can leave behind films and tacky residues that could cause bowlers to stick. Both scenarios are a recipe for disaster that could lead a bowler to an unplanned “Machuga Flop”. And while a flop can be funny, we all know it can hurt and it’s uber embarrassing. But, what is a bowling center to do? How can you maintain the delicate balance of not too slick and not too sticky? We’ve got the answers to your approach maintenance questions.
Some history
Before there were synthetic approaches, all approaches were made of wood and coated with a finish that allowed for proper slide. The only real maintenance to be done to these approaches was the occasional spot cleaning for spills and sticky marks and daily dusting. Then, once every year or so, the approach needed to be sanded and recoated to “refresh” the finish. Wooden approaches have a fairly even slide as long as the finish isn’t worn down. Once the finish started to wear, the approach could be spotty. Generally though, this was just an indication that it was time to refinish the approaches.
Synthetic approaches were introduced when synthetic lanes were introduced. Synthetic approaches were virtually maintenance-free since they eliminated the need for refinishing - or so it was thought. Synthetic approaches came with their own set of problems.
Think of synthetic approaches like your kitchen countertops; not the granite, marble, Corian, and fancy varietals, but the Formica and laminate variety. Layers of materials are pressed or bonded together and an outer layer with the approach image is pressed or bonded to the top. The top layer on which a bowler will slide is often textured and porous. This means dirt and residues can get into those tiny pores and cause build-up. It also means that repeated sliding in the middle of the approach can wear down the texture and cause inconsistencies in the slide-ability of the approach from the middle to the sides.
Because of these issues, a variety of different products and procedures have been developed to help bowling centers maintain their approaches. And what was once billed as an approach that was basically maintenance-free has now become even higher maintenance.
So what’s the right way to maintain synthetic approaches?
If I were to ask 50 different people the proper way to maintain the approach, I’d likely get many different answers. There would be variations of cleaning techniques that used various cleaners and solutions and even just hot water. There would be dust mops, wet mops, buffers, and spot cleaners. The only consistent thing would be that bowlers still complain and the approaches are inconsistent. It’s a vicious and never-ending cycle.
Synthetic approaches require temperature and humidity control. I did some digging, well, Googling, and I found that humidity over 50% can cause approaches to be tacky. We all know tacky isn’t good when trying to slide. To combat this, having some temperature control in the bowling center is absolutely necessary. Additionally, having circulation that pulls or pushes moist air away from the lanes/approaches can help keep moisture from the air from settling onto the approach. The optimal humidity is around 40%.
Dusting the approaches is a necessary task. Dust can settle on the approach and get embedded in the pores. Aside from just causing the approach to look dirty, dust can cause inconsistent slide-ability as well. Dust can cause approaches to be slick and, well, too slick is just as bad as too tacky.
Spills happen
It’s important to clean the spills and wipe away residues. Lane conditioner, soda, beer, and an infinite number of other materials can be spilled on the approaches and every one of them can cause sliding issues. When something is spilled on the approach, wipe it up as soon as possible with a clean, dry cloth. Use a weak dilution of cleaner to remove any sticky liquids. Go back over the area with another clean towel and some IPA (isopropyl alcohol). IPA is very good for removing sticky residues and leaves no residue behind of its own. It isn’t a “cleaner” but it will help remove sticky residues.
Clean those carpets and floors!
The carpets and flooring areas around the bowler’s circles must be kept clean as well. Wax from tiles and residues from carpets and carpet treatments can stick to shoes and can easily be tracked onto the approach. It’s just as important to keep the non-bowling areas clean as it is to keep the bowling areas clean. And, be careful what products you choose for cleaning. Many cleaning products leave behind residues and, as I said before, the residues can easily be tracked onto the approach.
The quest for consistency...
When all of this is done, sometimes you still need some help getting consistent slide on your approaches. There are many products on the market designed to help you with this. Unfortunately, so many of the products available have their own sets of issues. When sprayed, they can get on the lane surface and cause issues with the lane conditioner and pattern.
Dust type products can leave dust residue on the lane and the residue can settle in nearby areas. Some products have to be used very sparingly or the approach can end up being too slick. Some products work great when you first use them, but then after a couple of games, the approach is inconsistent again because the product has “worn off” in the slide area leaving the outsides slick and the slide area tacky.
All of this can be a big frustration. And, it’s one of the common complaints that we hear when dealing with approach questions. People just want a process that is simple and they just want the approaches to be consistent. In fact, I’ve heard from many bowlers that they wouldn’t mind the approaches being a little on the slick side or even a little on the tacky side as long as the approaches could be consistent from the ten pin side to the seven pin side. Bowlers can adjust for a little more slide or a little more stick. But, it’s nearly impossible to adjust when there isn’t any consistency across the approach.
To sum it up, synthetic approach maintenance can be tricky. It can be time consuming and tedious. And, with all of the approach maintenance products available, it can be downright overwhelming. But, the good news is, it doesn’t have to be. Giving your bowlers consistent approaches doesn’t have to be such a mind-boggling task. You can give your bowlers the left-to-right consistency they want on a day-to-day basis with Balance, Kegel’s new synthetic approach maintenance product. To learn more about Balance, click here.
How can a simple water filter become so clogged?
Anyone that maintains lane machines knows how critical routine maintenance is. But one item that often gets overlooked in lane machine upkeep are supply tank filters - the filters in the oil supply tank, filters in the cleaner supply tank, and now with the FLEX lane machine, the water supply tank filter (see help video below). In this feature article of the Inside Line, we’ll focus on the water supply tank and how those filters can become clogged over time, even though it’s "just water".
Most people are aware that all water is not created equal. Water can be hard or soft, and have different levels of calcium, phosphates, nitrates, sodium, potassium, and chloride, along with some uninvited guests depending on the water treatment plants. These substances are known as Total Dissolved Solids (TDS).
TDS is a measure of the “combined content of all inorganic and organic substances contained in a liquid in molecular, ionized, or micro-granular suspended form.” In layman’s terms, TDS is a measure of the amount of the stuff in the water you can’t see.
Knowing the TDS is all well and good but, how will this affect your lane machine filter?
Well, when water sits around, you know that mold and fungus can grow on the water’s surface. The water can become very pungent; you can actually see things growing and the water color changing. Think about bird baths and small fountains that don’t have running water; the stagnant water eventually turns rancid from mold and fungus growth.
When water sits in a container for long periods of time, a bio-film will eventually begin to form. Bio-films form on surfaces like tank walls and filters. Actually, they will form on virtually every non-shedding surface in a non-sterile or very humid environment.
On your teeth, plaque is a bio-film. In your cooling and heating system, bio-film forms reducing the effectiveness of the system. The slimy stuff you see on rocks and pebbles in streams is bio-film. In stagnant pools of water, bio-films can form on the surface.
Basically, a bio-film can form just about anywhere as long as there is a place for the cells to attach; the cells can attach to a solid surface or to each other.
So bio-films form in water, right? Well, why don’t bio-films form in bottled water at the grocery store?
Bottled water is packaged to prevent bio-films from forming. The bottled water you buy from the store is packaged under nitrogen pressure to force out the air. This prevents bio-films from forming in the water while it sits on the shelf. Once the bottle is opened and air is introduced to the system, the bio-film can begin forming. This is one reason why you shouldn’t reuse bottles from bottled water without thoroughly cleaning them.
Bio-film goes through five stages of development:
1. Initial attachment,
2. Irreversible attachment,
3. Maturation I,
4. Maturation II,
5. Dispersion.
The picture below shows how a bio-film develops through each of the different stages.
Five stages of bio-film development
Water quality in a specific location will dictate how fast a bowling center will have bio-film develop. TDS and the specific treatment methods used at the local water treatment facilities will change the water quality. Eventually though, every center will have to clean and/or replace their lane machine water filter at some time.
Just like your coffee maker at home, the water filter and supply tank should be cleaned periodically to prevent the problem. If you never clean your coffee maker, eventually the pump will fail. If you never clean your water supply tank in your single cup machines, a bio-film can form in the water tank.
At Kegel, we recommend removing and cleaning the water supply tank filter once a month. We also suggest flushing out the water supply tank at least every couple months, no matter how often you use your lane machine. The water is sitting in the supply tank the same amount of time no matter how many lanes you are doing a day – always.
This is what happens when filters are not maintained regularly:
A filter that has not been maintained.
If periodic maintenance is not being performed on a simple item like your water supply tank and filter, or any filter for that matter, the liquid in the tank will not flow properly and that will change your dilution ratios. We know changing dilution ratios will change ball motion. But, improper cleaning can also lead to a host of other issues.
Just like Sanction Technology has done for the oil system with process verification, with Kegel’s sprayless cleaner system it's easy to check volume output for water and cleaner. As we always say, “it’s better to know than to hope”, and as any lane person will tell you, it's also better for you to find any issues before your bowlers do.
Does lane oil evaporate and how long should the oil pattern sit?
When it comes to lane conditions, every person has their own ideas as to what they think works best. Mechanics, proprietors, and bowlers all have a difference of opinion when it comes to dressing the lanes. Ask 100 different people and you’re likely to get 100 different answers. In bowling, it’s one of those topics that just seems to create a lot of controversy and a lot of differences in opinions.
Because of all these different opinions, we get many questions regarding what the best methods are for ensuring lanes are the same from day to day. Some of these questions stem from curiosity while others, like the one I got last month, stem from bowler controversy.
I was forwarded a message that came in from our website. The proprietor was quite frustrated at his bowlers because his bowlers felt like the lanes were getting conditioned too early and the conditioner was “drying up” before they ever started bowling. The proprietor tried to show the bowlers statisitical data in their score trends that suggested otherwise. But, the bowlers just didn’t agree. So, he asked “the experts”; how long can an oil pattern sit on a lane before it starts to deteriorate?
Modern lane conditioners; every lane conditioner available in today’s market; are all mineral oil based. Kegel uses pharmaceutical grade mineral oil in our lane conditioners so it is of the highest purity available. Mineral oil itself doesn’t evaporate. You could fill a cup with mineral oil and leave it sitting and it wouldn’t evaporate. Here is a link to a safety data sheet (SDS) for white mineral oil. If you look in section 9 (page 4 of the document), it shows the evaporation rate as ‘NA’. This means there is negligible or no evaporation of the material.
There are some chemicals in lane conditioners that will evaporate but these ingredients are minor compared to the percentage of mineral oil. For example, solvents such as isopropyl alcohol (IPA) are often used as an inexpensive way to lower the surface tension. Lowering the surface tension will allow the lane conditioner to wet across the lane surface more quickly. Once the lane conditioner is applied, the IPA would evaporate over time. Since lane conditioners are applied in such a thin film with a low volume over a larger area, we would estimate this to be in the 30 minute range at most. It does not take a lot of IPA to lower the surface tension so it is used in amounts of 1% or less. This evaporation does not affect the lane play characteristics that come from the mineral oil and the other ingredients that are used to give the conditioner its characteristics.
While we’ve never tested the theory of how long a lane conditioner could sit before deterioration begins, a lane pattern could sit, well, forever without deteriorating. That is, of course, in theory since we don’t have a time machine! There are other things; environmental and atmospheric conditions; that will affect lane conditions. But, the conditioner itself could sit for days on the lane and it would still be there; it isn’t going to evaporate away.
While we haven’t tested the ‘forever’ theory, we have allowed a freshly conditioned lane to sit for 24 hours. We took tapes from the freshly applied pattern and took tapes on the same pattern 24 hours later. The results: the tapes were exactly the same for both sit times. The conditioner sitting on the lane didn’t change as a result of evaporation.
Other things can affect the conditioners performance though. Dust from the air or from AC vents can be deposited on the lane. These particles can greatly affect the playing characteristics of the pattern. This is one reason that a good cleaning routine is so important. Applying lane conditioner to a dirty lane will also affect the playing characteristics of the pattern.
Atmospheric conditions like temperature and humidity will also greatly affect lane play and these are more likely the cause of changing lane conditions. Bowling centers see this a lot as the weather changes, especially when there are sharp changes from cold to hot or hot to cold. Bowlers will complain that the lanes are tighter or drier or something else but they don’t always consider the weather changes and that can affect lane conditions significantly.
Here are two previous Inside Line articles that address changing weather and lane conditions: The Weather’s Changing… Are Your Lane Conditions? and Lane Conditions and Cold Snaps.
How long a conditioner should be allowed to sit on a lane prior to bowling is a very common question. And, it’s one that we’ve gotten many times. While consistency is key, we like to support our arguments with science. So, here’s a little science behind conditioner application.
When lane conditioner is immediately applied to a bowling lane, several things must happen before the lane conditioner stabilizes enough to provide consistent playing characteristics. One is allowing the lane conditioner to adhere to the lane surface. This takes about 15-30 minutes depending on the amount of conditioner applied, the type of conditioner, the type of cleaner being used, and the surface energy of a particular lane surface.
The surface tension of the conditioner is also important since the surface tension directly affects how the conditioner “wets” across the lane. The conditioner needs to “like” the lane in order for it to wet across. If the surface energies between the two don’t agree, the conditioner will “sit up” on the lane surface (think of this effect as little beads of water sitting on the surface of your car versus the water sheeting off the surface of the car).
Another bonding takes place within the lane conditioner molecules themselves. These bonding forces, known as van der Waals forces, are basically weak attractions between atoms, molecules, and surfaces. The time for this to take place after conditioning a bowling lane is also anywhere from 15-30 minutes. The below video shows these weak bon
With the amount of lane conditioner being used in today's lane patterns, it takes about 15-30 minutes for the lane conditioner to "settle down" and stabilize on the lane. If time is not allowed for this process to take place, things like excessive carrydown can occur. The lanes may also play "tighter" simply because the oil is sitting up on top of the lane more and there is less resistance to the bowling ball as it rolls through the oil pattern. This is one reason; during tournaments where we provide lane maintenance; we always try to get the tournament organizers to allow a minimum of 15 minutes of lane conditioner "sit time" before the first ball is thrown down the lane.
The biggest key is consistency. It’s one of the things that we preach. Create a routine and stick with that routine every day. If you do the lanes an hour before league, do them an hour before league every time and you’ll eliminate that variable (and that complaint from your bowlers).
We hope this information helps you. If you have additional questions, please feel free to contact us. We will be happy to assist in any way we can. Until next time, happy bowling!
Getting your Pinsetter Ready for the New Season
Maintenance to your pinsetter is important to keep your center running smoothly. In this article, we will discuss some commonly overlooked maintenance items and some tips to help you prepare for your winter season.
Pin Damage
Sometimes pin damage can be easily explained as in the examples below, but some can be much more troublesome to find. Small marks and scratches can accumulate so slowly over a period of time that irreversible damage sneaks up on you and can handicap the appearance, as well as the performance, of the pin.
QUICK TIP: Before you install a full set of new pins for the Fall Leagues, first start with installing one single pin in each pinsetter and run for a shift. Remove the new pin and examine it. If there is any damage, remove the pin and tag the machine for a more in depth inspection.
Usually if pins are getting damaged and showing marks, you can locate the problem area by the evidence of pin chips or shavings. Loose or broken parts tend to scratch the pins, so inspecting all pin delivery paths should lead you to the problem.
Common Problems:
-Pin deck area - Screws, flat gutters, edge boards, and kickback plates
-Broken turret wires and missing deck rollers (A-2)
-Misadjusted turret wires can lead to damage from pulley or center chute (A-2)
-Broken or loose parts on the bin assembly (AMF)
-Missing ball wheel guards (A-2)
-Cracked plows (AMF)
These are just a few examples, but the most important thing to remember is that your problems should be fixed immediately before you risk damaging a new set of pins.
Ball Lifts - See what you can “uncover” before Leagues start!
Ball lifts can easily become overlooked throughout the season since they are an efficient piece of equipment. They run pretty much trouble free so the old saying, “Out of sight, Out of mind!” fits here. Simply doing a quick cleaning and inspection can eliminate the chance of unexpected downtime or ball damage.
Inspection:
-Make sure the lift turns on properly when either pinsetter is powered up
-Inspect belt and belt tracking
-Inspect ball lift tires
-Listen for any unwanted noises
-Check for loose hardware
After the ball lift is cleaned, insert two balls in the trap doors, push them into the lift, and watch the transition through the lift. The balls should move up freely with no belt slippage.
Secondly, with the lift off, take a single ball and manually rotate the top pulley to feed the ball through the lift. The ball should transition through the contact points of the two tires and C track smoothly. If you get binding or slipping spots through the transition, you may need to look at your upper and lower tire configuration.
There are several different kinds of tires and each of these have their own characteristics. Mixing and matching tires in a lift can also create different transition characteristics, so find a combination that works well for your center. Smooth consistent transition is the goal here. A binding lift can cause premature belt wear and may also lead to too much motor strain and amp draw, eventually causing the relays to fail.
By performing regular maintenance and catching problems early, you can help keep your center running at its top performance.
Learn about Kegel Pinsetter Parts
Switching Lane Conditioners: Out with the old, in with the new!
Bowl Expo has come and gone once again. That means that summer is in full swing and league season will be upon us before you know it. As such, you may be thinking about trying a new lane conditioner, like Fire or Ice, before league season starts. These conditioners were released last year and they have been gaining attention because of their performance in tournaments and championships worldwide. Now is the perfect time to try one and get your pattern adjusted to be ready for fall.
Changing lane conditioners can be an overwhelming process. In fact, just the thought of it may send shivers down your spine. After all, if your bowlers have been happy, why change it and risk upsetting the balance? Well, technology has come a long way. We’ve worked hard developing conditioners that will help you protect your lane surface while providing a durable lane condition for your bowlers. And, we’ve improved the durability while allowing you to use less conditioner which saves you money.
Once you’ve decided to make the leap (and decided which conditioner to use – we’ll have more on that later), you’ll need to spend some time cleaning your lane machine. While it may seem easy to just empty the conditioner tank and pour in the new conditioner, you won’t be doing yourself any favors by doing this. Cross contamination from one conditioner to another in the same tank can wreak havoc on your lane pattern and make your lanes inconsistent. And that just leads to unhappy bowlers. No one wants that!
Additionally, some lane conditioners just don’t mix well with others.* This can cause things like clogged tubing, pencil tips, or even oil control valves. You can avoid a lot of headaches by taking some extra steps early on.
*The FLEX Lane Machine boasts the ability for centers to use two compatible conditioners simultaneously. Currently, Fire and Ice are the only compatible conditioners that can be used in this manner. Mixing other conditioners, such as Prodigy or Infinity, with Fire or Ice is not recommended.
Changing conditioners in the machine is a tedious process, but it is a process that is well worth it. Here is a brief overview of the process for Sanction Technology™ lane machines:
Remove the conditioner tank from the lane machine. Empty the contents of the tank into a waste container.
Use some lane cleaner to clean the conditioner tank. Add some of your lane cleaner solution directly to the tank. Swirl or shake the cleaner to get it all over the inside of the tank.
Rinse the tank with water. You’ll want to shake and swirl to be sure the tank gets completely clean. Continue rinsing until the water is clear (it will probably look milky at first) and there is no foam.
Rinse the tank with some acetone (if available) and let the tank dry. It is best to let the tank dry overnight, but give it as much time as possible. The tank needs to be completely dry before you add new conditioner.
Use this time to wipe down and perform any maintenance to the transfer system. This is also a good time to perform some cleaning and/or maintenance to the buffer brush.
Place the conditioner tank back in the machine.
Now you’re ready to fill the conditioner tank and flush the machine. We’ve detailed the entire process here: Changing Out Conditioners - Sanction Technology
So, I’m ready to fill my machine and flush the lines, but I don’t know which conditioner to use. Don’t worry; we’re here to help!
Fire and Ice have similar properties chemically but they yield different results on the lane. Both conditioners are pinsetter and house ball friendly meaning that you’ll have fewer issues in the backend. Both conditioners also have improved durability even with reduced volume.
There are a few factors that can help you decide which would be best for you. What conditioner do you use now? What is your lane surface? Do you have more open play or do you have heavy league and tournament lineage? Answering all of these will help narrow down which option will be best for your situation. Every center is unique, so as always, our Tech Support Team is available to guide you. You can also use the comparison chart below to help in your decision.
Now that you’ve got your new conditioner into your machine and ready to go, we always recommend running your normal pattern and watching ball reaction before adjusting anything. This way you’ll have an apples-to-apples comparison from conditioner to conditioner. It is highly likely, based on our experience with Fire and Ice, that pattern adjustments will be necessary.
To reap the benefits of these conditioners, your pattern should have good front to back taper. If you’re pattern doesn’t have good taper, our Tech Support Team can help you make some adjustments to maximize the performance of these conditioners. If you’re pattern does have good taper, some small adjustments may be all you need to dial in your pattern. Here are some of the common adjustments we’ve seen:
Reduced pattern volume (i.e. 50 ul to 45 ul or 40 ul)
Average pattern volume is 10-20% lower with Ice and 10-15% lower with Fire
Shortened pattern distance and/or reverse buffer drop
Reduction of applied loads
Don’t let the fear of upsetting your bowlers stop you from trying something new. You can reap the benefits of Fire and Ice with a little patience. Start now and you have the rest of the summer to fine-tune before fall leagues. You’ll enjoy the rewards of your hard work and patience when your bowlers are happy with the more durable lane conditions and you have less oil-related backend issues.
Learn more about Fire and Ice Lane Conditioners