Bowling Bedlam - The Lane
The playing environment of bowling today may be as complex, unpredictable, and chaotic as any time in the history of the game. We’re not talking about the recreational league or club game where the participants just want to have fun, and the conditions are designed as such. We’re talking about professionally maintained and controlled tournament environments where bowling sports people compete.
It is in this type of sporting environment, along with the basic premise of playing well physically and mentally, that the decisions the modem player makes will ultimately determine whether they perform up to their expectations or have to wait until the next event comes around.
The players of today have to choose how to execute their delivery using which type of bowling ball, with which layout, with what surface preparation, on what lane surface, with what lane characteristic, on which oil pattern, and following what group of players. The player must also change this strategy rapidly and often during any specific round of play or throughout the course of an event.
This series of articles will try to shed some light on many of the variables in the current game of bowling and why the players of today need to be very open minded and aware of the total environment at all times when competing. The supplied information is all in the quest of understanding and to increase performance, not to create excuses.
The Lane
There is no question bowling balls of today are more frictional, hook more, and cover more area across the lane as it travels from the foul line to the pins. The modern core designs and coverstock compositions create more friction, which also makes the bowling ball more responsive to all the different variables that make up the playing environment.
There are different types of plastic film coated wood lanes which are the softest lane surfaces. There are wood lane surfaces coated different types of urethane which are the next hardest lane surfaces. The hardest and most common lane surfaces around the world now are synthetic lanes, with many different installation and friction characteristics.
We won’t get to deep into the specific manufactured hardness, friction, or wear properties of synthetic lanes, but keep in mind that all manufactured synthetic lane surfaces are different and how those surfaces wear from use is also not equal.
The USBC has performed studies that show some modern synthetic lane surfaces score best when brand new, some score better after a few years, peak, and then begin to score worse, while other surfaces score higher as wear and friction increases.
In regard to topography, the sanding techniques on wood lanes make those lanes much flatter than that of the installation of multiple synthetic panels. When a particular bowling center employed a strict resurfacing program, with skilled resurfacers, all the lanes in the bowling center was of high-quality and fairly consistent.
It is therefore a fair statement to say that wood lanes that are consistently resurfaced, screened, and re-coated on a consistent basis are more level than the synthetic bowling lanes of today.
One might think the contrary when only thinking about the synthetic panel itself. But when multiple panels are attached in sections on top of structures made up of other wood components, and more often than not on top of older wood foundations, it is easy to see the challenge for consistent levelness across a center using synthetic overlays. But it’s not impossible to achieve.
The current lane specification rules were written in 1937 by the American Bowling Congress, for wood lanes. The basics of the rule are the entire lane must be less level within plus or minus 40/1000 of an inch to be certified and approved for sanctioned play. The idea was that any groove deeper than the specification would allow too much guidance, or path correction, of the bowling ball after it was released by the bowler.
These level number limits also apply to crowns (hills), depressions (valleys), crosswise tilts, and lengthwise levelness. Surprisingly, only recently has the lengthwise level specification been added into the rules. The 40/1000 inch specification now reads “over 42 inches in any direction”, but only for new installations or centers that are changing from wood lane surfaces to synthetic overlays.
However, the overwhelmingly majority of the lanes are still inspected and passed by inspecting the lanes at only three predetermined points. These three inspection points are at a distance from the foul line between 10’-15’, 30’-40’ and 50’-55’. It is of course at these predetermined inspection areas installers of synthetic lanes pay most attention to.
Of course there are some very good installations and installers of synthetic lanes today but the reality is, installations are only as good as the time and care that is taken on a particular installation. Since the advent of synthetic lanes, achieving consistent levelness throughout a bowling center is a very difficult painstaking task and the tools and technology to level lanes in a more efficient manner have not been available. (Note: The recent invention of the Kegel Portable LaneMapper has made this process more efficient and attainable.)
Long time laneman and former PBA Lane Maintenance Director Len Nicholson states, “I’ve seen synthetics installed in 4-6-hours and they were legal according to the Sanctioning Body. This was in bowling centers that were changing over to synthetic overlays after their wood surfaces have reached their life limit. However, when the arena settings started on the PBA Tour and companies like AMF and Brunswick wanted to showcase their synthetic lanes, it would take them up to two days to get them as perfect as they could. And they were using their best installers performing the job on only four lanes!”
As the bowling ball travels down the synthetic lanes of today, it has to go slightly uphill sometimes, and then downhill at other times. The ball encounters random patterns of hills, valleys, and it encounters microscopic frictional differences, all without any uniformity.
By performing tests at the Kegel Training Center’s adjustable lanes in 1999 with top PBA professionals such as Parker Bohn III, Brian Voss and Jason Couch, it was proving that as little as 20/1000 of an inch, or 25 percent of the allowable tolerances, will affect the path and reaction of today’s highly responsive bowling balls.
These seemingly minute irregularities can cause a ball to increase its footprint which increases the friction between the ball and the lane. This will make the ball slow down more therefore increasing the hook potential. These topographical irregularities may also decrease the footprint between the ball and the lane which causes less friction. This makes the ball slow down less therefore decreasing the hook potential.
These random irregularities can make your intended shot possibly either hit the pocket heavy, light or in extreme cases even miss the pocket entirely.
When oil patterns that are designed to play more towards the outside portion of the lane are applied to bowling lanes which are predominantly crowned on the outside boards, it is difficult for the bowling ball to hook back into the pocket. Most short oil patterns are designed this way, and crowned lanes can make those patterns more difficult. However on longer oil patterns, or patterns designed to play more towards the inside portion of the lane, crowned lanes can sometime act like hold area which can increase mistake area.
On the other hand, bowling lanes that are depressed from the edge board can act like a race track with high banked turns on short oil patterns. The highest scoring lanes for short oil patterns are when lane topography is either slightly depressed or flat.
On long patterns however, depressions can take away hold area and make a long pattern more difficult since the ball will have a tendency to hook more. That is unless the player is on the other side of the depression. Then a depressed lane acts like that same banked race track a depression gives a player on a short pattern.
Unfortunately, rarely do synthetic lanes have a consistent character with regard to topography which makes it a challenge for both the players and the laneman.
For tournament players, depending on what lane a player begins their round on, these lane differences may determine a player’s equipment choice for the day or even where to play with no likeness of another. These choices can and often will cause the oil pattern to change in a different manner from day to day, squad to squad, pair to pair and even lane to lane.
A scenario often seen in leagues and tournaments throughout the world is when there are perceived differences in ball reaction, total blame is put on the oil condition when in fact most times it is the difference in the topography, surface friction of the lanes, or even the bowler themselves.
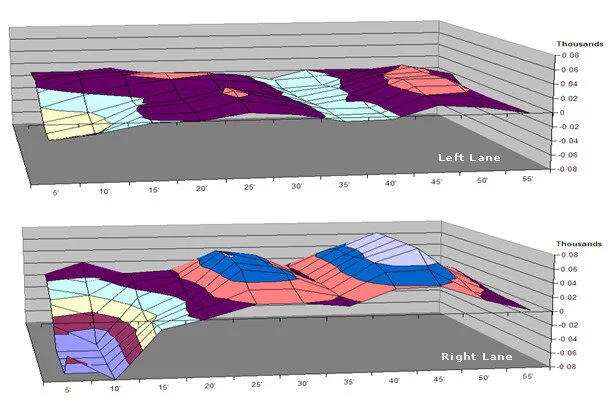
The below picture show a real world example of two lanes that make up a pair in a sanctioned bowling center.
The left lane of the pair is within specification, plus or minus 40/1000 inch, at most points throughout the lane. The right lane however has historically played notably different than its companion.
In this case, because of the extreme depression in the head area, and the excessive crowns in the mid lane and break point area of the lane, the right lane has always played considerably tighter. Basically the bowling ball is falling off the mountain in the midlane and then trying to climb the mountain as it begins it move towards the pocket. The depression in the head area also causes the ball to 'burn up' earlier which causes less back end movement. The players in this center say they are always lined up 4-5 boards different between these two lanes with the ball hooking much less on the right lane.
Take notice the points on the right lane that are within specification, which in this example are not many but only in the three aforementioned inspection areas. The left lane is also most level in those same three inspection areas.
Kegel has measured 1000’s of lanes and studied the scores of many different tournaments they have been associated with. They have found these topographical and frictional differences are the reason those “mystery pairs” tend to show up at bowling centers. It’s not always that those lanes or pairs are bad or out of specification and sometimes that one lane or those mystery pairs are actually flatter than all the other lanes. What makes them challenging is they are different than the others and players are trying to adjust to that one different lane off of all the others.
With all other things being equal, low scoring centers or tournaments are more about the lane surfaces throughout center being very irregular from lane to lane, while higher scoring can be more about the lane surface being very consistent from lane to lane.
In short, when centers have consistent topographical features from lane to lane, fewer adjustments from the players are needed.
Nicholson tells of an example from the PBA Tour at The Showboat in Las Vegas; “The TV Pair always played weird. The great PBA players always had problems. Scores on that pair were never up to par and eventually they changed the TV pair.”
If there is one thing you can take from this article, is to look at bowling lanes individually with each having their own unique characteristics. Don’t look upon a pair of lanes as both being the same or adjust to one lane in a pair off of the other lane unless you notice a specific trend in the center.
The balance between caring for the playing environment and it participants from the monetary pressures is one of bowling's sanctioning bodies’ greatest challenges. Our recreational fads will come and go with having to be continually reinvented to keep interest amongst those non-sporting customers. A healthy sport of bowling however will produce lifelong customers which every business person should want to create and sustain.